4. Formation Control¶
4.1. Introduction¶
The formation control function arranges the actions of multiple robots connected to the same LAN, using the plaintext SDK for overall control. Users can use this function to implement more complex actions and implement attractive formation movement.
This function works by connecting multiple robots to the same LAN in Wi-Fi router mode, allowing you to communicate with these robots by using Python scripts on your PC while sending plaintext SDK commands in order to implement formation control. The following simple example explains how to implement formation control by using a Python script through the plaintext SDK.
4.2. Environment¶
- Hardware devices: a router, two EP robots, and a PC
- Python version: Python 3.6
4.3. Establish a multi-device connection¶
Set the EP robots to operate in Wi-Fi router mode and, in the app, connect the robots for formation control to the router one by one. After successfully establishing the connection, go to the connection page in the app settings and record the IP addresses of the robots. For detailed instructions, refer to Wi-Fi router mode.
4.4. Run the sample program¶
Enter the IP addresses in the IP_LIST list in the sample code and save the script code as ep.py.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89
#!/usr/bin/env python3 # coding=utf-8 import sys import time import threading import socket IP_LIST = ['192.168.1.103', '192.168.1.117'] EP_DICT = {} class EP: def __init__(self, ip): self._IP = ip self.__socket_ctrl = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM) self.__socket_isRelease = True self.__socket_isConnect = False self.__thread_ctrl_recv = threading.Thread(target=self.__ctrl_recv) self.__seq = 0 self.__ack_list = [] self.__ack_buf = 'ok' def __ctrl_recv(self): while self.__socket_isConnect and not self.__socket_isRelease: try: buf = self.__socket_ctrl.recv(1024).decode('utf-8') print('%s:%s' % (self._IP, buf)) buf_list = buf.split(' ') if 'seq' in buf_list: self.__ack_list.append(int(buf_list[buf_list.index('seq') + 1])) self.__ack_buf = buf except socket.error as msg: print('ctrl %s: %s' % (self._IP, msg)) def start(self): try: self.__socket_ctrl.connect((self._IP, 40923)) self.__socket_isConnect = True self.__socket_isRelease = False self.__thread_ctrl_recv.start() self.command('command') self.command('robot mode free') except socket.error as msg: print('%s: %s' % (self._IP, msg)) def exit(self): if self.__socket_isConnect and not self.__socket_isRelease: self.command('quit') self.__socket_isRelease = True try: self.__socket_ctrl.shutdown(socket.SHUT_RDWR) self.__socket_ctrl.close() self.__thread_ctrl_recv.join() except socket.error as msg: print('%s: %s' % (self._IP, msg)) def command(self, cmd): self.__seq += 1 cmd = cmd + ' seq %d;' % self.__seq print('%s:%s' % (self._IP, cmd)) self.__socket_ctrl.send(cmd.encode('utf-8')) timeout = 2 while self.__seq not in self.__ack_list and timeout > 0: time.sleep(0.01) timeout -= 0.01 if self.__seq in self.__ack_list: self.__ack_list.remove(self.__seq) return self.__ack_buf if __name__ == "__main__": # Instantiate the robots for ip in IP_LIST: print('%s connecting...' % ip) EP_DICT[ip] = EP(ip) EP_DICT[ip].start() for ip in IP_LIST: EP_DICT[ip].command('gimbal moveto p 0 y 0 vp 90 vy 90 wait_for_complete false') time.sleep(3) while True: for ip in IP_LIST: EP_DICT[ip].command('gimbal moveto p 0 y 45 vp 90 vy 90 wait_for_complete false') time.sleep(3) for ip in IP_LIST: EP_DICT[ip].command('gimbal moveto p 0 y -45 vp 90 vy 90 wait_for_complete false') time.sleep(3) for ip in IP_LIST: EP_DICT[ip].exit()
Run the script.
- For Windows: After installing the Python environment, click ep.py to start the script.
- For Linux: Enter “python ep.py” on the CLI to start the script.
- View the running performance.
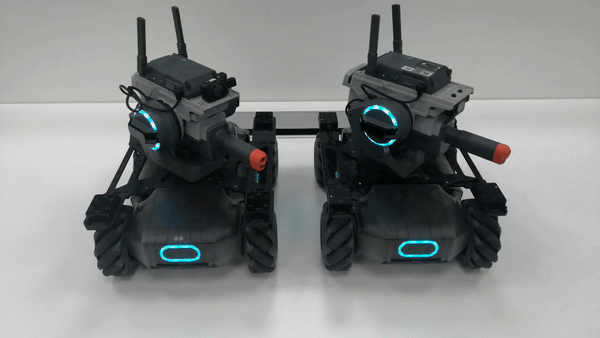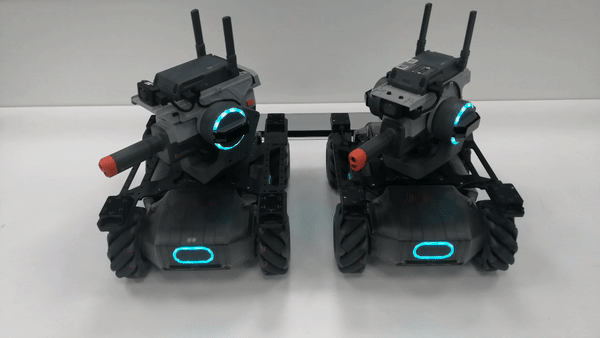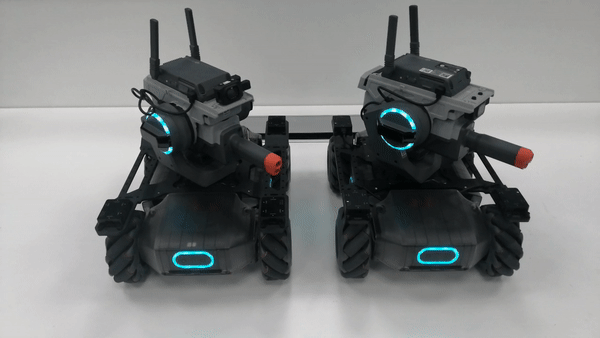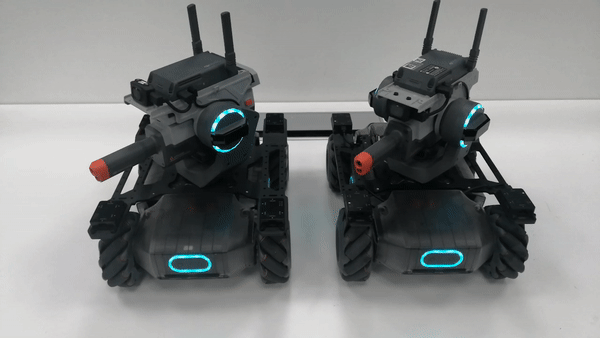
The gimbals of the robots for formation control move together in the yaw-axis direction.
- View the running result.
The command-line port outputs cleartext communication data between the robots and the host.